

Most later color circles include the purples, however, between red and violet, and have equal-sized hue divisions. The divisions of Newton's circle are of unequal size, being based on the intervals of a Dorian musical scale. The original color circle of Isaac Newton showed only the spectral hues and was provided to illustrate a rule for the color of mixtures of lights, that these could be approximately predicted from the center of gravity of the numbers of "rays" of each spectral color present (represented in his diagram by small circles). In his book Opticks, Isaac Newton presented a color circle to illustrate the relations between these colors. This includes those of the Natural Color System. Some colour wheels are based on the four opponent process colors - red, yellow, blue and green. There is no authoritative way of labelling the colors in such a color wheel, but the six colors which fall at the corners of the RGB cube are given names in the X11 color list, and are named keywords in HTML. The outer top circle of the HSV cylinder – or the outer middle circle of the HSL cylinder – can be thought of as a color wheel.
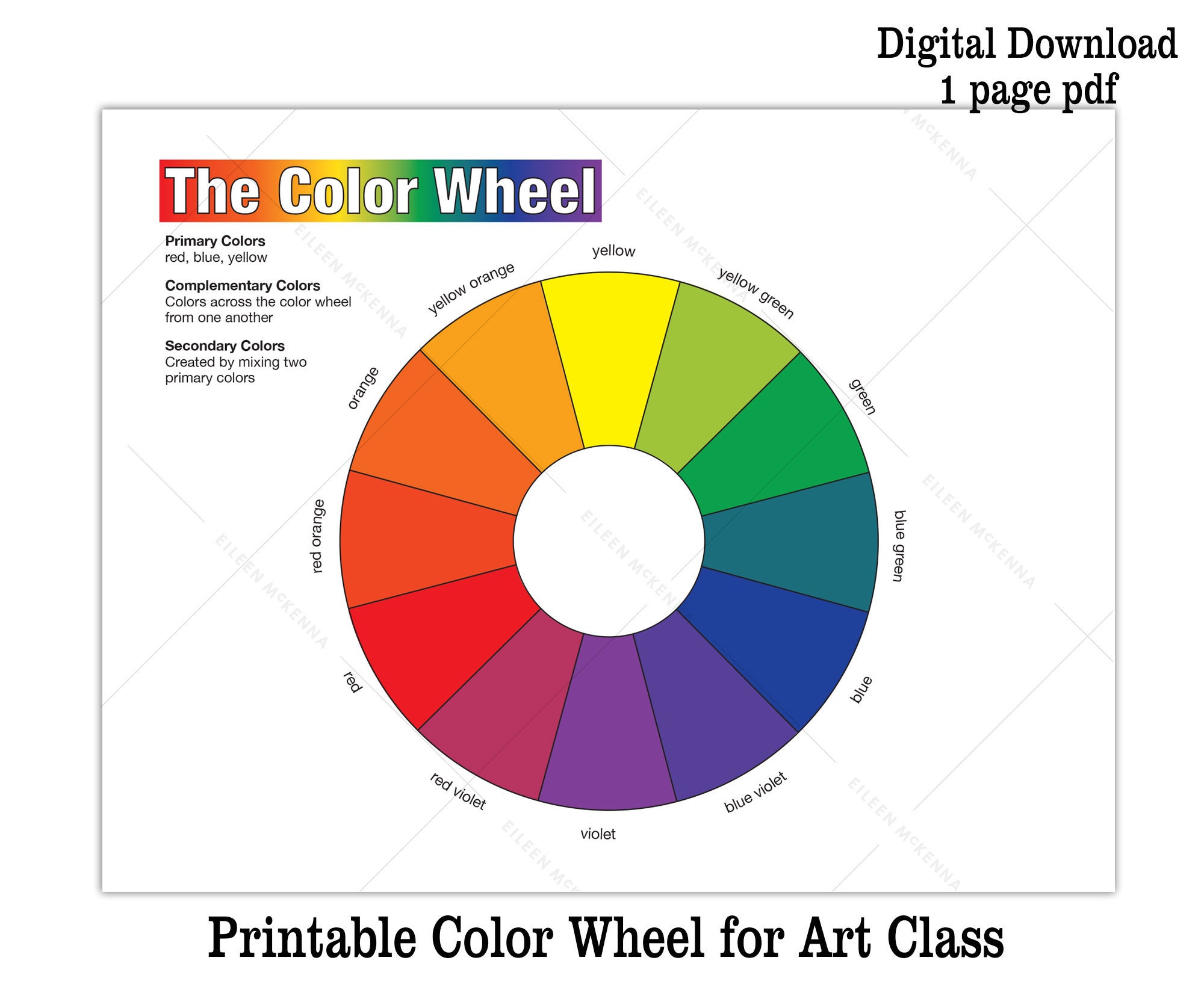
The HSL and HSV color spaces are simple geometric transformations of the RGB cube into cylindrical form. In an additive color circle, the center is white or gray, indicating a mixture of different wavelengths of light (all wavelengths, or two complementary colors, for example).Ī color wheel based on HSV, labeled with HTML color keywords. Sometimes a RGV (red, green, violet) triad is used instead. Alternatively, the same arrangement of colors around a circle can be described as based on cyan, magenta, and yellow subtractive primaries, with red, green, and blue being secondaries. In a paint or subtractive color wheel, the "center of gravity" is usually (but not always ) black, representing all colors of light being absorbed.Ī color wheel based on RGB (red, green, blue) additive primaries has cyan, magenta, and yellow secondaries. Intermediate and interior points of color wheels and circles represent color mixtures. Printers and others who use modern subtractive color methods and terminology use magenta, yellow, and cyan as subtractive primaries. Non-digital visual artists typically use red, yellow, and blue primaries ( RYB color model) arranged at three equally spaced points around their color wheel. The tertiary colors are green-yellow, yellow-orange, orange-red, red-violet/purple, purple/violet-blue and blue-green.

The corresponding secondary colors are green, orange, and violet or purple. The typical artists' paint or pigment color wheel includes the blue, red, and yellow primary colors. A 1908 color wheel with red, green, and violet "plus colors" and magenta, yellow, and cyan blue "minus colors".


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
